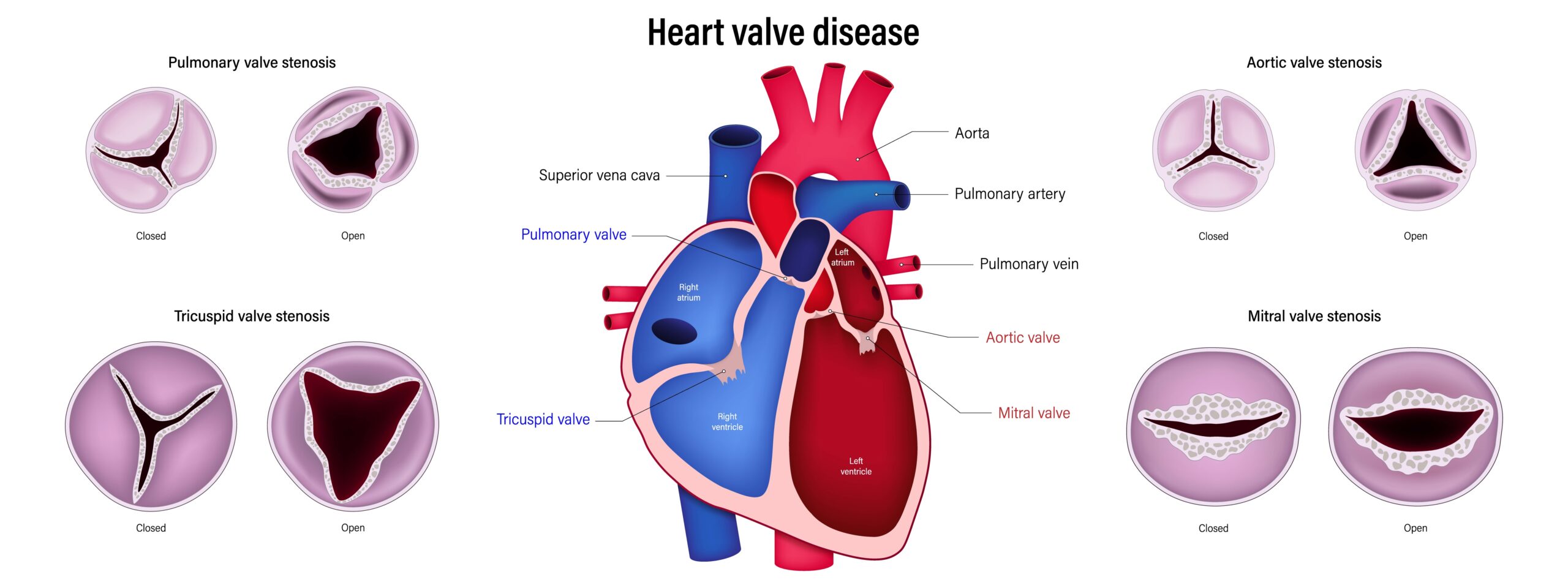
Heart valve disease encompasses a range of disorders affecting one or more of the valves in the heart. The heart has four valves: the mitral and aortic valves on the left, and the tricuspid and pulmonary valves on the right. These valves play a crucial role in directing blood flow through the heart’s chambers and to the rest of the body. When these valves don’t work properly, it can impact the heart’s efficiency and overall health. The main types of valve disease include stenosis (narrowing of the valve), regurgitation (leaking of the valve), and atresia (a valve that is not properly formed).
Causes
Heart valve disease can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired later in life. Acquired causes include age-related changes, infections (such as infective endocarditis), rheumatic fever, and conditions like heart attack or heart disease which can damage the valves or the heart tissue surrounding the valves.
Symptoms
Many people with heart valve disease do not experience symptoms for years. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms might include:
- Shortness of breath, especially with exertion or when lying down
- Fatigue
- Swollen ankles or feet
- Dizziness or fainting spells
- Irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Coughing, particularly at night or when lying down
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of heart valve disease usually involves a physical examination, during which a doctor may detect a murmur or other abnormal heart sounds. Diagnostic tests may include echocardiography (an ultrasound of the heart), which is the primary tool for diagnosing valve disease, electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, and cardiac MRI.
Treatment
Treatment for heart valve disease depends on the severity of the condition and the specific valve(s) affected. Options include medication, to relieve symptoms or to manage conditions contributing to valve disease; surgical repair, to fix the valve’s shape or to separate fused valve flaps; valve replacement, using either mechanical valves or biological tissue valves from pigs, cows, or human donors; and minimally invasive procedures, such as balloon valvuloplasty to widen a narrowed valve.
Prevention and Management
While congenital heart valve disease cannot be prevented, the risk of developing acquired valve disease can be reduced through general heart-healthy practices. These include regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and managing conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Outlook
The outlook for individuals with heart valve disease varies depending on the valve affected, the severity of the disease, and the treatment received. Many people lead normal or near-normal lives with treatment. Monitoring by a healthcare provider is essential to manage the condition effectively and to adjust treatment as necessary.
Heart valve disease is a complex condition that requires a thorough understanding for effective management. Advances in medical science have significantly improved the diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes for those affected by this condition, allowing many to live longer, healthier lives.